AWS All-in-one
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is used in Cloud Computing Intro.
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud: Amazon EC2
AWS for Data Science
AWS service for messaging, serverless computing, and containers
Messaging and queuing
Applications are made of multiple components.
- For example, there are monolithic applications = an application with tightly coupled components. If one component fails, other components fail.
- To help maintain application availability when a single component fails, we can design our application through a microservices approach
- In a microservices approach, application components are loosely coupled.
- Two services facilitate application integration
- Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS): a publish/subscribe service (subscribers can be web servers, email addresses, AWS Lambda functions, etc.)
- Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS): a message queuing service
Containerized applications
can be achieved by
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS): support Docker
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS): support Kubernetes
Serverless computing
- your code runs on servers, but you do not need to provision or manage these servers
- the flexibility to scale serverless applications automatically
- can be achieved by
-
ASW Lambda
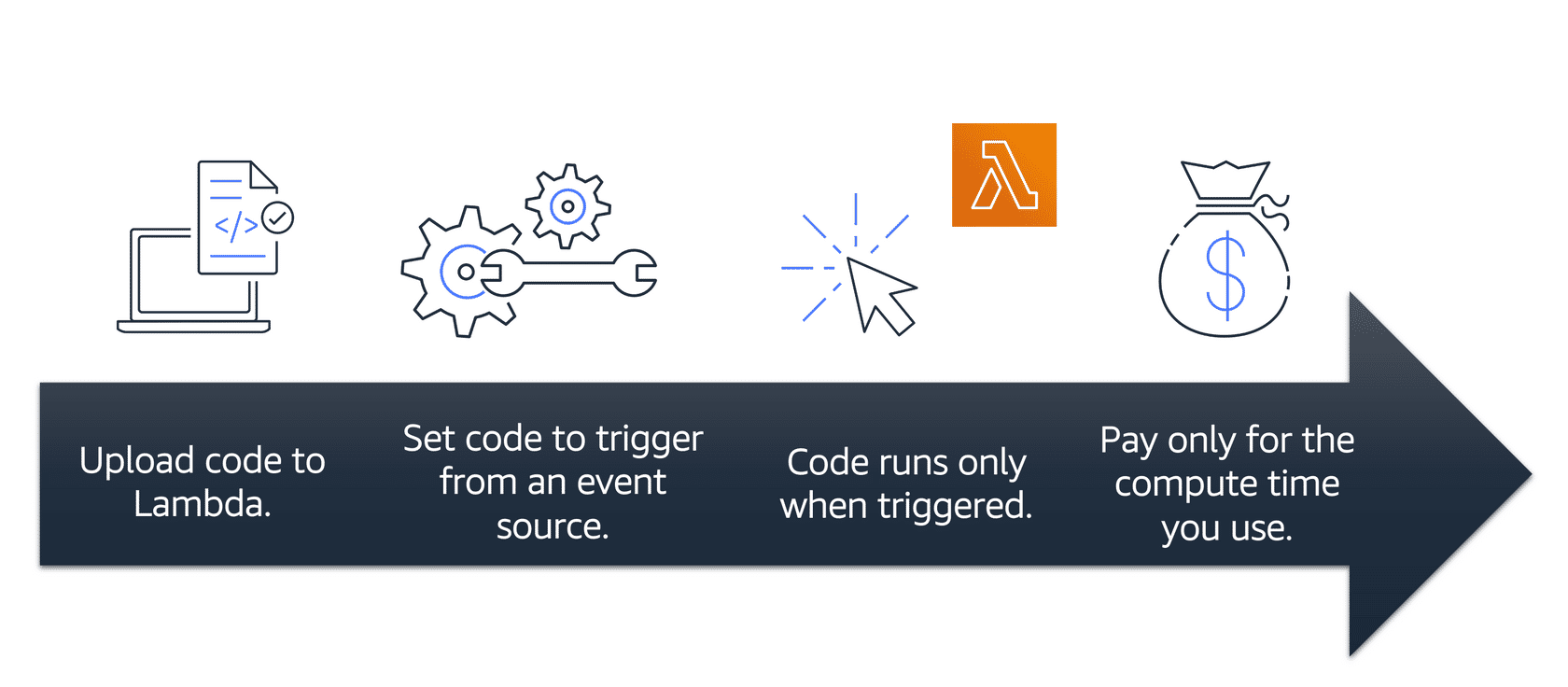
-
AWS Fargate: run your containers on top of a serverless compute platform
-
Ways to interact with AWS services
- AWS Management Console
- a web-based interface for accessing and managing AWS services
- AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI)
- automate actions for AWS services and applications through scripts
- Software development kits (SDKs)
- make it easier for you to use AWS services through an API designed for your programming language or platform.
- AWS Management Tools
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- you provide code and configuration settings, and Elastic Beanstalk deploys the resources necessary to perform the following tasks:
-
Adjust capacity
-
Load balancing
-
Automatic scaling
-
Application health monitoring
-
- you provide code and configuration settings, and Elastic Beanstalk deploys the resources necessary to perform the following tasks:
- AWS CloudFormation
- treat your infrastructure as code: you can build an environment by writing lines of code instead of using the AWS Management Console to individually provision resources.
- It determines the right operations to perform when managing your stack and rolls back changes automatically if it detects errors.
- AWS Outposts
- Extend AWS infrastructure and services to your on-premises data center.
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk